

On August 15, the National Bureau of Statistics released the latest industrial production data. Data show that in July, the domestic industrial robot output was 38183 sets, down 8.8% year on year; In the first half of the year, the production of domestic industrial robots was 238041 sets, a year-on-year decrease of 11.5%.
In terms of data, compared with the output of 46144 sets and increase of 2.5% in June, the production of industrial robots in July decreased .
This decline is also reflected in the overall changes in the manufacturing industry.
According to the changes in the manufacturing PMI index, in July, the Manufacturing Purchasing Manager Index (PMI) was 49.0%, down 1.2 percentage points from the previous month and below the critical point.
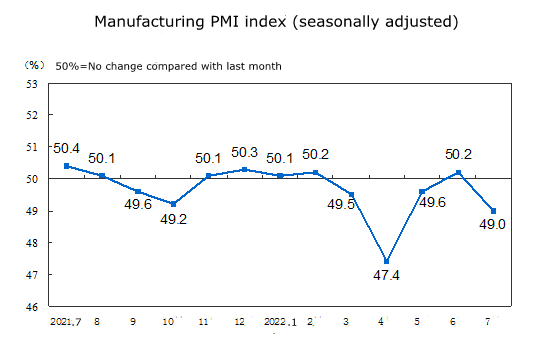
Note: the PMI index is above 50%, reflecting the overall economic expansion; Less than 50%, reflecting economic recession.
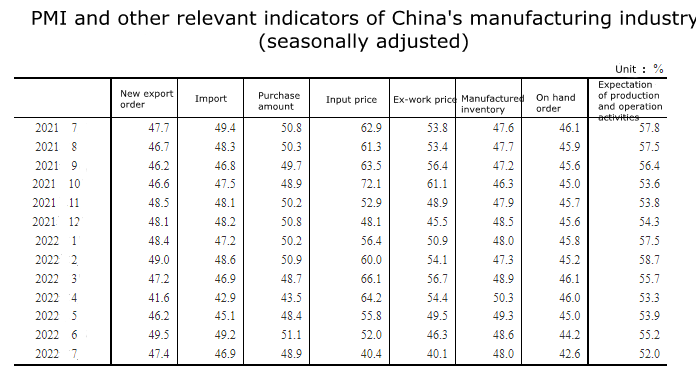
From the breakdown data of the index, 5 indexes constitute the PMI of the manufacturing industry, namely, the production index, new order index, raw material inventory index, employee index, and supplier delivery time index. The data of the 5 sub-indexes are:
The production index was 49.8%, down 3.0 percentage points from the previous month and below the critical point.
The new order index was 48.5%, down 1.9 percentage points from the previous month and below the critical point.
The raw material inventory index was 47.9%, down 0.2 percentage points from the previous month.
The employment index was 48.6%, down 0.1 percentage points from the previous month.
The supplier delivery time index was 50.1%, down 1.2 percentage points from the previous month, but still higher than the critical point.
It can be seen that, except for the delivery time index of suppliers, the other indexes are below the critical point, indicating that the production activities of the manufacturing industry have slowed down, the demand has dropped, and the inventory of main raw materials has continued to decrease, the employment climate of enterprises has slightly decreased, and the delivery time of raw material suppliers has slightly accelerated compared with last month. Among them, the production index dropped the fastest, indicating that the slowdown of manufacturing production activities is the main factor affecting the decline of the PMI index.
July is the traditional off-season of production. In addition, the repeated epidemics in many parts of the country, the summer flood season, the high temperature, and other adverse factors have caused the logistics to be blocked, resulting in the decline of the manufacturing industry at both ends of supply and demand. Second, although the shortage of raw materials and key parts caused by the control of the Q2 epidemic has been alleviated, it still exists. The production and operation of enterprises are under obvious pressure, the economic recovery is still fluctuating, and the recovery foundation is not yet solid.
But on the whole, there is no need to be pessimistic.
First of all, since the closure of epidemic control areas such as Shanghai and Jilin, there have been few large-scale and long-term outbreaks. The state has made a series of arrangements for the stable development of the macroeconomy. The industrial recovery expansion trend since May has taken shape.
Although the PMI index fell in July, the expected index of production and operation activities was 52%, still in the expansion range.
GGII's judgment on industry expectations also shows that with the control of the new round of epidemic, the shortage of parts, especially chips, has been alleviated in stages, and the output of industrial robots in China will increase slightly in the third quarter.
Specific to the current data, in July, the added value of industries above the designated size increased by 3.8% year-on-year (the growth rate of added value below is the actual growth rate after deducting the price factor). From a month-on-month comparison, in July, the added value of industries above the designated size increased by 0.38% over the previous month. From January to July, the added value of industries above the designated size increased by 3.5% year on year.
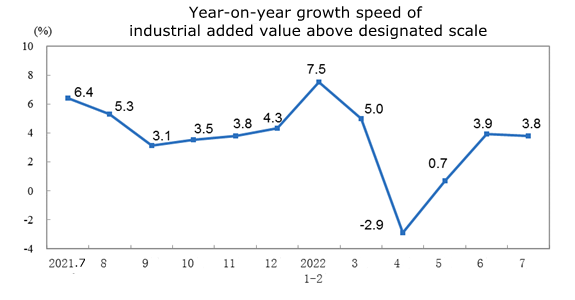
The overall industrial production still showed a recovery trend, of which the added value of the manufacturing industry increased by 2.7% year on year. As for the industries related to industrial robots, except the general equipment manufacturing industry, which dropped slightly by 0.4%, the special equipment manufacturing industry, automobile manufacturing industry, railway, ship, aerospace, and other transportation equipment manufacturing industry, electrical machinery and equipment manufacturing industry, computer, communication, and other electronic equipment manufacturing industry all achieved positive growth.
Among them, the performance of the automobile manufacturing industry is the most brilliant, with the year-on-year growth of added value reaching 22.5%, which is 6.3 percentage points faster than that of the previous month. The output increase of new energy vehicles has reached 112.7%.
Automobile manufacturing is one of the important terminal industries supporting the order demand for industrial robots. The doubling of the output of new energy vehicles is expected to bring a strong driving effect to the growth of the demand for industrial robots.
Therefore, although the output of industrial robots has decreased compared with June, it is only a phased contraction, which is a sign that the economic recovery has not been stable. With the overall recovery of industrial production and the strong pull of terminal industries such as new energy vehicles, the recovery of industrial robot output in the third quarter is still worth looking forward to.
